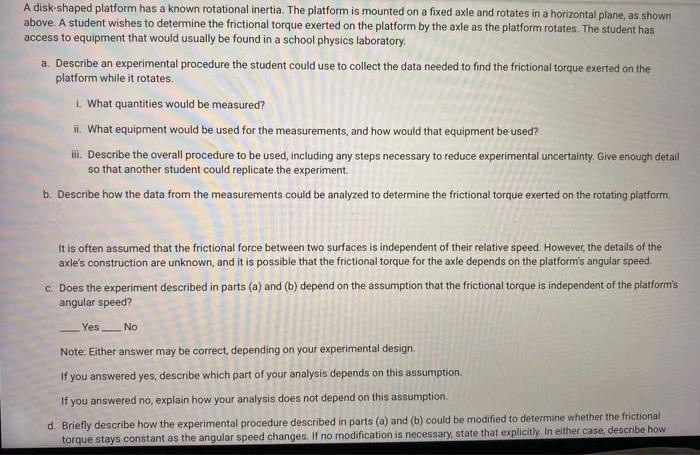
A disk shaped platform has a known rotational inertia frq. This inherent property plays a pivotal role in the performance and applications of disk-shaped platforms, making it an essential consideration in their design and analysis.
Understanding the concept of rotational inertia and its impact on disk-shaped platforms is crucial for engineers and designers seeking to optimize these platforms for specific applications.
Rotational Inertia of Disk-Shaped Platforms

Rotational inertia, a crucial property of disk-shaped platforms, measures their resistance to angular acceleration. Understanding and calculating rotational inertia is essential for analyzing and designing these platforms in various applications.
The rotational inertia (I) of a disk-shaped platform is given by the formula: I = (1/2) – m – r^2, where m is the mass of the disk and r is its radius.
Factors affecting the rotational inertia of a disk-shaped platform include its mass, radius, and thickness. A more massive disk with a larger radius will have a higher rotational inertia.
Applications of Rotational Inertia in Disk-Shaped Platforms, A disk shaped platform has a known rotational inertia frq
- Flywheels:Disk-shaped flywheels store rotational energy, providing stability and reducing fluctuations in speed.
- Turntables:Turntables use the rotational inertia of disk-shaped platforms to provide a stable surface for rotating objects.
- Gyroscopes:Gyroscopes rely on the rotational inertia of disk-shaped platforms to sense and maintain orientation.
Measurement and Analysis of Rotational Inertia
Methods for measuring rotational inertia include using a torsional pendulum or a rotating table. Accurate measurement is crucial for predicting platform performance.
Software tools and techniques are available for analyzing rotational inertia, providing insights into platform dynamics and behavior.
Design Considerations for Disk-Shaped Platforms with Known Rotational Inertia
When designing disk-shaped platforms with known rotational inertia, factors to consider include:
- Material selection:Different materials have different densities, affecting mass and rotational inertia.
- Shape optimization:The shape of the disk can be optimized to achieve desired rotational inertia.
- Balancing techniques:Balancing is crucial for reducing vibrations and ensuring smooth operation.
FAQ Insights: A Disk Shaped Platform Has A Known Rotational Inertia Frq
What is rotational inertia?
Rotational inertia is a measure of an object’s resistance to angular acceleration. It is analogous to mass in linear motion.
How is rotational inertia calculated for a disk-shaped platform?
The rotational inertia of a disk-shaped platform can be calculated using the formula I = (1/2)MR^2, where I is the rotational inertia, M is the mass, and R is the radius.
What factors affect the rotational inertia of a disk-shaped platform?
The rotational inertia of a disk-shaped platform is primarily affected by its mass, radius, and thickness.