Art-labeling activity the distribution of spinal nerve branches – Art-labeling activity, a groundbreaking technique in spinal nerve branch distribution analysis, offers invaluable insights into the intricate organization and function of these neural structures. This innovative approach empowers researchers to trace and visualize the intricate pathways of nerve branches, unraveling their precise distribution patterns and shedding light on their role in sensory and motor functions.
Through art-labeling experiments, researchers meticulously inject tracer substances into specific spinal nerve branches. These tracers, meticulously selected for their ability to selectively label neuronal elements, are then meticulously transported along the nerve fibers, illuminating their intricate branching patterns. By analyzing the distribution of labeled nerve branches, scientists can construct detailed maps of the spinal nerve network, providing a comprehensive understanding of their organization and connectivity.
1. Overview of Art-Labeling Activity
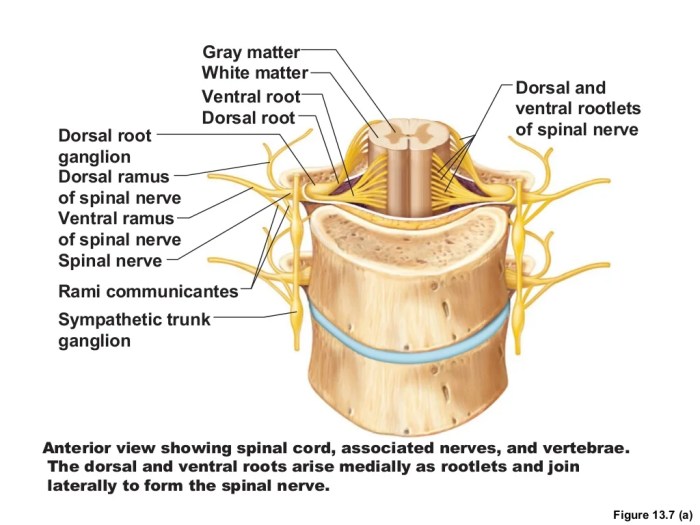
Art-labeling activity is a technique used to trace the distribution of nerve branches in the spinal cord. It involves injecting a tracer into a specific nerve branch and then examining the tissue to determine where the tracer has traveled. This information can be used to create a map of the nerve’s distribution, which can be helpful for understanding the organization and function of the spinal cord.
Art-labeling techniques have several benefits over other methods for tracing nerve distributions. First, they are highly sensitive, allowing researchers to detect even small changes in nerve distribution. Second, they are relatively non-invasive, meaning that they can be performed without causing significant damage to the tissue.
Third, they are relatively easy to perform, making them a good choice for researchers who do not have extensive experience with neuroanatomy.
2. Methods and Procedures: Art-labeling Activity The Distribution Of Spinal Nerve Branches
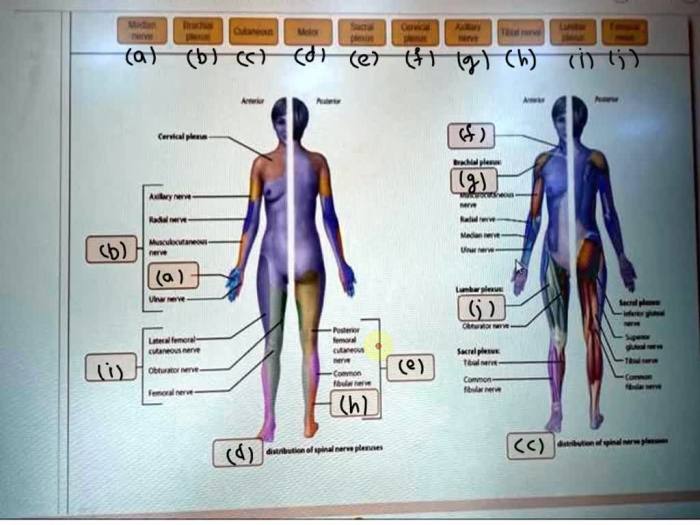
The steps involved in performing an art-labeling experiment are as follows:
- Prepare the tissue. The tissue must be fixed in a solution that will preserve the nerve fibers. This can be done by immersion in a fixative solution or by perfusion with a fixative solution through the blood vessels.
- Inject the tracer. The tracer is injected into the nerve branch that is being studied. The tracer can be a dye, a radioactive isotope, or a fluorescent protein.
- Process the samples. The tissue is processed to make the tracer visible. This can be done by staining the tissue with a fluorescent antibody or by exposing the tissue to X-rays or other forms of radiation.
3. Results and Observations
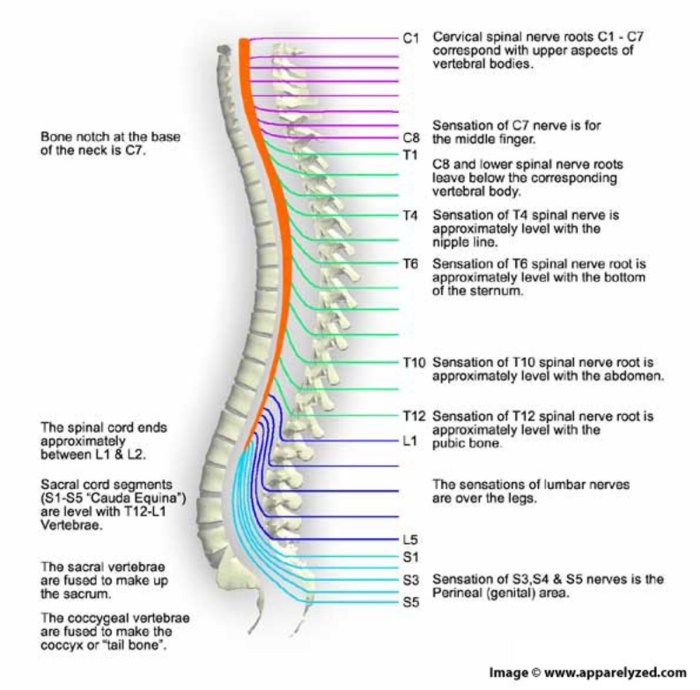
The expected outcomes of an art-labeling experiment are a map of the nerve’s distribution. This map will show the location of the nerve’s cell bodies, axons, and dendrites. The map can be used to identify the nerve’s target organs and to understand how the nerve interacts with other nerves in the spinal cord.
The distribution patterns of labeled nerve branches can be interpreted in a number of ways. For example, the density of labeled fibers in a particular area can be used to infer the relative importance of that area to the nerve.
The presence of labeled fibers in an unexpected location can indicate that the nerve has a wider distribution than previously thought.
4. Applications and Implications
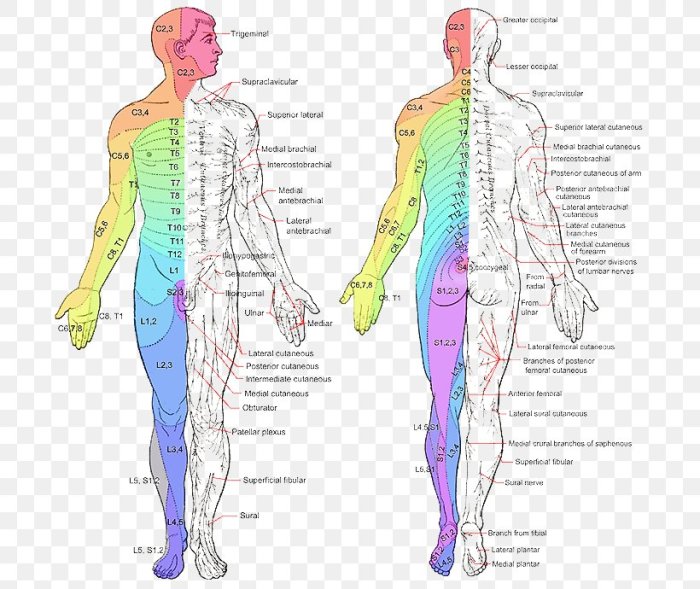
Art-labeling techniques have a wide range of applications in understanding the organization and function of spinal nerve branches. These techniques can be used to study the development of the spinal cord, the effects of injury on the spinal cord, and the mechanisms of pain transmission.
The findings from art-labeling experiments have important implications for clinical practice and research. For example, these findings can be used to develop new treatments for spinal cord injuries and to improve the diagnosis and treatment of pain.
Popular Questions
What are the advantages of using art-labeling in spinal nerve branch distribution analysis?
Art-labeling offers several advantages, including precise labeling of specific nerve branches, visualization of intricate branching patterns, and the ability to study the distribution of nerve branches in intact tissue.
How does art-labeling contribute to clinical practice?
Art-labeling findings can guide surgical interventions by providing detailed maps of nerve branch distribution, minimizing the risk of nerve damage and optimizing functional outcomes.